TYPES
of NETWORKS
LAN connects networking devices with in short spam of area, i.e. small offices, home, internet cafes etc. LAN uses TCP/IP network protocol for communication between computers. It is often but not always implemented as a single IP subnet. Since LAN is operated in short area so it can be control and administrate by single person or organization.
WAN - Wide Area Network
As “word” Wide implies, WAN, wide area network cover large distance for communication between computers. The Internet itself is the biggest example of Wide area network, WAN, which is covering the entire earth. WAN is distributed collection of geographically LANs. A network connecting device router connects LANs to WANs. WAN used network protocols like ATM, X.25, and Frame Relay for long distance connectivity.
Wireless - Local Area Network
A LAN, local area network based on wireless network
technology mostly referred as Wi-Fi. Unlike LAN, in WLAN no wires
are used, but radio signals are the medium for communication. Wireless network
cards are required to be installed in the systems for accessing any wireless
network around. Mostly wireless cards connect to wireless routers for
communication among computers or accessing WAN, internet.
MAN - Metropolitan Area Network
This kind of network is not mostly used but it has
its own importance for some government bodies and organizations on larger
scale. MAN, metropolitan area network falls in middle of LAN and WAN, It covers
large span of physical area than LAN but smaller than WAN, such as a city.
NETWORK TOPOLOGY
In computer networking, topology
refers to the layout of connected devices. This article introduces the standard
topologies of networking.
Network topologies are categorized
into the following basic types:
1.
BUS topology
 - uses a single
backbone segment (length of cable) that all the hosts connect to directly. The
idea is that is just like riding a bus. It has only one driver and many
passengers who are riding.
- uses a single
backbone segment (length of cable) that all the hosts connect to directly. The
idea is that is just like riding a bus. It has only one driver and many
passengers who are riding.
2. RING topology
-connects one host to the next
and the last host to the first. This creates a physical ring of cable.
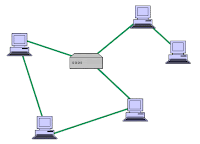
3. STAR topology
– connects all cables to a
central point of concentration. This point is usually a hub or switch. It has a
focal point where all the resources are there.
4. MESH
topology
– is used when
there can be absolutely no break in communications. So as you can see in the
graphic, each host has its connections to all other hosts. This also reflects
the design of the internet which has multiple paths to any one location.


No comments:
Post a Comment